Water is an essential resource for all living beings on Earth. However, with the increasing human population and industrialization, the availability of clean and safe water is becoming scarce. This has led to the need for effective wastewater treatment plants that can purify contaminated water before it is released back into the environment.
In this blog post, we will take a closer look at wastewater treatment plants and the process involved in purifying the flow of water.
The Importance of Wastewater Treatment Plants
Wastewater treatment plants are essential for maintaining a healthy ecosystem. They not only help to protect public health but also safeguard our environment. Without proper treatment, sewage and industrial waste can cause severe pollution and pose a threat to aquatic life, plant life, and even humans.
Furthermore, wastewater treatment plants are also crucial for conserving water resources. By purifying the flow of contaminated water, they ensure that it can be safely reused for various purposes such as irrigation, industrial processes, and even drinking.
The Process of Wastewater Treatment
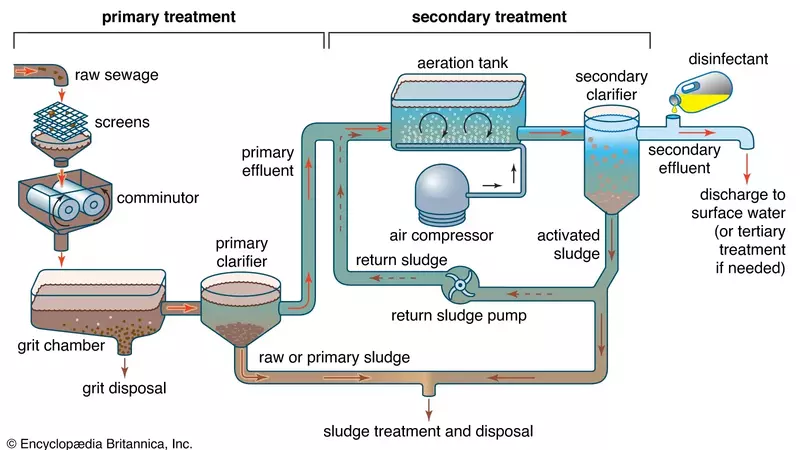
Wastewater treatment involves several physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove contaminants from the water. The exact process may vary depending on the type of wastewater being treated and the level of purification required. However, most treatment plants follow a similar process which can be divided into three main stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment.
Primary Treatment
The first stage in wastewater treatment is known as primary treatment. In this stage, large objects such as rocks, sticks, and other debris are removed from the water. This crucial step is accomplished by passing the water through a series of screens and grit chambers.
But how is this process carried out accurately and efficiently? By implementing ultrasonic level sensors! These sensors help to determine the levels of water in tanks, ensuring that the water is moving through the screens and grit chambers at the right pace. This ensures that the large objects are effectively removed, laying the foundation for the remainder of the wastewater treatment process.
Secondary Treatment
The second stage, also known as secondary treatment, involves biological processes to remove organic matter and nutrients from the water. The most common method used in this stage is called the activated sludge process, where microorganisms are introduced into the wastewater to break down any remaining organic matter. This results in cleaner water and reduces the amount of pollutants that can harm aquatic life.
Tertiary Treatment
The final stage of wastewater treatment is tertiary treatment. This stage involves additional processes to further purify the water and make it safe for reuse. These may include chemical treatments such as chlorination, zonation, or ultraviolet (UV) disinfection to kill any remaining bacteria and viruses. Some plants also use advanced technology such as reverse osmosis or membrane filtration to remove any remaining impurities.
Inside a Wastewater Treatment Plant
Now that we have covered the main stages of wastewater treatment, let’s take a closer look inside a typical treatment plant to understand how it all works together.
Inlet Works
The first step in the treatment process is known as inlet works. This is where the raw sewage enters the plant from various sources such as homes, businesses, and industries. The sewage is then screened to remove any large objects and debris before being pumped into the primary treatment tanks.
Primary Treatment Tanks
Once inside the primary treatment tanks, the flow of water slows down, allowing small particles to settle at the bottom while oils and grease rise to the surface. These are skimmed off and sent for further treatment. The remaining water then moves on to the next stage.
Secondary Treatment Tanks
In the secondary treatment tanks, microorganisms are added to digest any remaining organic matter and nutrients. This process creates a layer of sludge at the bottom of the tank which is then pumped out for further processing.
Tertiary Treatment Process
The final stage in the treatment process involves additional treatments such as disinfection and filtration to remove any remaining impurities. After this stage, the purified water is ready to be discharged back into the environment or reused for various purposes.
The Future of Wastewater Treatment Plants
As our population continues to grow, so does the water demand. This puts a strain on our limited resources and highlights the importance of wastewater treatment plants in ensuring water sustainability. However, with advancements in technology and a growing focus on environmental protection, the future of these plants looks promising.
Some treatment plants are now incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power to reduce their carbon footprint. There is also ongoing research and development into more efficient and cost-effective methods of wastewater treatment.
Conclusion
Wastewater treatment plants play a vital role in maintaining a healthy environment and preserving our precious water resources. Through various treatment processes, these plants purify contaminated water and make it safe for reuse or discharge back into the environment. As we continue to face challenges related to water scarcity, it is crucial to invest in sustainable and innovative solutions like wastewater treatment plants to ensure a better future for all living beings on Earth.